Federated Chaumian eCash for Bitcoin Lightning
Chaumian eCash is a cryptographic concept developed by David Chaum in 1982, which is applied to Bitcoin Lightning.
In this article, we explain how eCash can ensure that the Lightning network continues to scale and become more private and secure as custodial services for users.
We explain how payments are processed via Chaumian eCash, what benefits eCash offers for the Lightning network, and what implementations can help you run your own eCash Mint.
On the German YouTube channel of Coincharge you can find a video about Chaumian eCash for Bitcoin Lightning with English subtitle.
Scaling Bitcoin transactions
The Bitcoin network can only process 6-7 transactions per second, and with Segwit and optimal utilization of the blocks on the blockchain, the limit is likely to be a maximum of 1 million transactions per day. This will never be sufficient to be used as a global payment network.
Second layer solutions can provide a remedy here. With the Lightning network, there is a solution with another layer (second layer) that is based on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Second layer solutions, such as the Lightning network, bypass the need for final confirmation at the base layer, but even this solution has limitations.
This is because if every Lightning Node for every opening and closing of a channel is also done via the Bitcoin Blockchain, then a maximum of 1 million channels can be opened or closed per day.
In the meantime, there are approaches to solutions, such as batch opening or channel factoring, where multiple Lightning channels can be opened and closed with one transaction on the blockchain.
Custodial Services for the Lightning Network
However, the question also arises as to whether each user of the Lightning network also needs to operate their own Lightning Node with multiple Lightning channels. To send and receive Lightning payments, a custodial Lightning wallet such as the Wallet of Satoshi can be used.
In a Custodial Lightning Wallet, users share a common Lightning Node and its channels, which is operated by a Custodial.
It is recommended to use a self-custody solution, such as a dedicated hardware wallet, for the saved Bitcoin. For daily Bitcoin payments of smaller amounts, using a custody service may be a better solution.
With a custody service, internal payments and transfers are not recorded on the Bitcoin Blockchain and do not need to be routed over the Lightning network. Thus, transactions outside of Blockchain and Lightning network are possible.
The use of a custody provider is interesting for any Lightning user who does not want to run their own Lightning Node.
Lightning users are willing to store some sats with a custody provider, but this requires trust in the custody provider.
Custodial services offer significant scaling potential outside of blockchain and the Lightning network, but there is a risk that there will be a concentration on a few custody providers (e.g., custodial Lightning wallet providers).
If there is a centralization of custodial providers, this will likewise lead to a concentration of customer funds and customer data.
More competition among providers, smaller providers, greater privacy for users, and safekeeping of customer funds can help reverse these centralization trends.
Chaumian eCash for Bitcoin Lightning offers a solution for this.
What is Chaumian eCash?
Chaumian eCash is based on the idea of cypherpunk and cryptographer David Chaum. The latter described the concept of the “blind signature” in the 1982s and developed a payment system called eCash based on these findings.
The original eCash concept of blind signature is adopted by Chaumian eCash (Federated eCash) and applied in such a way that it can be used for shared managed Bitcoin wallet.
The central authority is a so-called Mint, as custodian of Bitcoin assets for third parties.
We can think of an eCash Mint as a kind of Custodial Lightning Bank that holds Bitcoin Lightning funds of its customers.
Custodial providers hold and manage client funds under their own complete supervision.
In contrast to this complete external safekeeping (custody), with an eCash mint the safekeeping takes place under the administration of a community.
As a distinction between custody and self-custody, this joint eCash custody can be referred to as shared custody or community custody.
Fedimint refers to the administrative form of an eCash mint as a federation. Here, all operations and postings are performed by a quorum of nodes controlled by different parties. Due to the federation approach, it is also referred to as Federated Chaumian Mint or Federated Mint.
Payment processing at an eCash Mint
An eCash mint accepts bitcoin deposits from its users and exchanges them into bitcoin or sats denominated eCash tokens.
These bitcoin, meanwhile, are stored in a multisig address shared by a number of custodians, reducing custodial risk.
To use an eCash mint, an associated eCash wallet is required. The eCash Mint user can make deposits and withdrawals to this eCash wallet via the Lightning network.
The users of the same eCash Mint, can make payments among themselves without making these payments through the Lightning network. These internal eCash mint transactions are cheap and can be performed indefinitely.
The operator of an eCash mint, does not know the owners of the eCash wallet, i.e. its users. An eCash mint does not know the number of users, their identity, account balances or transaction histories.
An eCash Mint thus offers Bitcoin and Lightning network users privacy, scalability, and security features that complement each other perfectly.
Anyone can set up or support their own eCash Mint. This gives users complete freedom to choose the Mint with the best reputation, or to use a local Mint with which to personally interact with members of the depository.
These federated or community mints are an ideal solution for local communities. The community establishes a common Mint and allows its members to deposit funds and pay anyone who has an eCash wallet connected to the Mint.
Anyone can run such a Mint for their friends or as a group. The community around the blocktrainer or einundzwanzig could run a common mint, under control of some trusted members. All users would be able to settle payments among themselves with Mint’s own eCash token and likewise make external payments via the Lightning network.
Likewise, platform operators such as Facebook, Twitter or Telegram could become operators of an eCash Mint, or regional providers such as a regional newspaper or local bank.
Lightning deposit at an eCash Mint
Let’s say a user wants to make a deposit of 1,000 sats at an eCash Mint. For this, the payer creates a message comparable to a check for 1,000 sats.
This message is put into an envelope and sealed. This means that the message is encrypted by the creator of the message and can only be opened again by him, i.e. decrypted.
The envelope is made of carbon paper and everything written on the envelope copies itself to the message inside.
The eCash Mint receives this encrypted message, but cannot see what is inside the envelope. The eCash Mint receives a payment of 1,000 sats and signs the outside of the envelope with the words “Whatever this secret is, it is worth 1,000 satoshis.”
The carbon paper transfers the signature from the envelope to the message (check) as well.
The eCash-Mint server does not know the contents or the owner of the envelope and returns the blinded signature with the message inside.
The user receives back the envelope encrypted by him, with the signature of the Mint. Since he encrypted the message, only he can decrypt it, i.e. open the envelope.
The message inside now bears the signature of the Mint.
If the user removes (decrypts) the signed message from the envelope, a token is generated in the process. This token is stored in the wallet and represents the equivalent of 1,000 Sats.
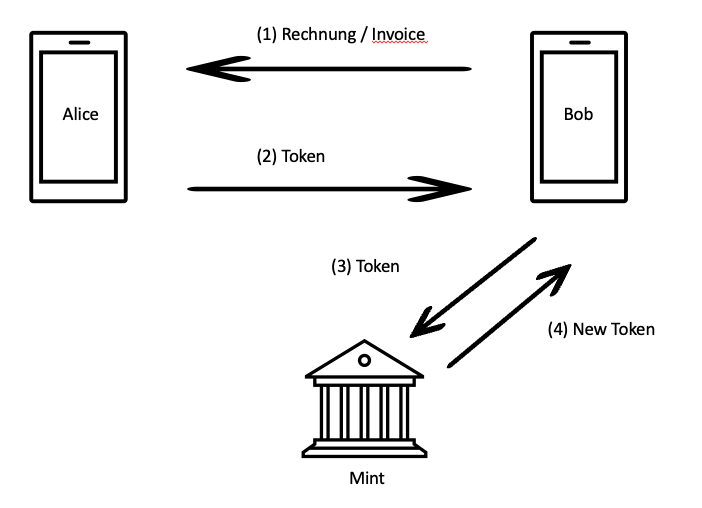
Payment within an eCash Mint – from eCash Wallet to eCash Wallet
- Bob creates an invoice and sends the invoice to Alice
- Alice sends the eCash tokens to Bob
- Bob sends the tokens to the Mint. There the tokens are checked and destroyed
- Mint creates a new token and sends this new token to Bob.
To settle the payment, the recipient submits the eCash tokens to the Mint and asks to exchange them for new eCash tokens.
This prevents the tokens from being issued twice.
The eCash-Mint recognizes the validity and value of the token through its own signature, destroys this token and creates a new token, and sends them to the recipient of the payment.
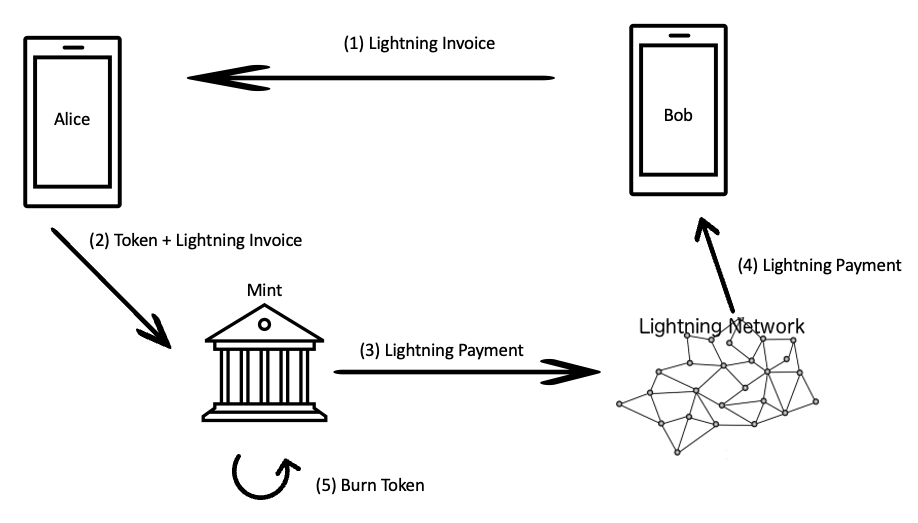
Pay a Lightning Invoice via eCash Wallet
- The Lightning merchant or the recipient of the Lightning payment creates a Lightning invoice and sends the Lightning Invoice to the payer (in this case Allice).
- The payment is to be made via the eCash wallet and sends the payment order to the Mint.
- Mint makes the Lightning payment through its Lightning gateway.
- Over the Lightning network, the Lightning payment is routed and the Lightning Invoice is paid by Bob.
- The eChash tokens used for the Lightning payment will be destroyed by Mint.
Advantages of eCash for Lightning
Not everyone wants to or can operate their own Lightning Node
If you want to send and receive Lightning payments, you either have to operate your own Lightning node (self-custody) or turn to a provider who takes over the entire service but has access to the Sats in return (custody).
The main advantage is that you don’t have to run your own Lightning Node to send and receive Lightning payments. You don’t have to go to a central, anonymous custodial provider; there may be small local providers that offer this service.
Running a Lightning Bank can be done for friends and acquaintances, but platform operators, communities and banks can also offer this service for their own customers, members and friends.
Increase of Lightning transactions in the Lightning network
The Bitcoin Blockchain is currently capable of performing approximately 1 million transactions per day. Using Lightning, the number of transactions can be expanded infinitely, but opening and closing a Lightning channel requires one transaction on the blockchain at a time.
If every Lightning user were to open one or more Lightning channels with their Lightning Wallet, this could become problematic as Lightning adoption grows in the future.
Therefore, one criticism of the Lightning network is that if more and more users use the Lightning network, then opening and closing Lightning channels may push the Bitcoin blockchain to its limit.
By sharing Lightning Nodes, there are no limits to the growth of the Lightning network.
Privacy
A Mint does not know its users, their balances or the transactions made. Thus, there is anonymity towards the operator of the Mint. But also outside of Mint results in a higher anonymity for the user. All Lightning payments from users of a Mint are perceived externally as total activity of that Mint.
Usability
Unlike a self-managed (self-custody) Lightning Wallet, a managed (custody) Lightning Wallet offers a friendlier user experience and handling. This is also the case for Ecash Lightning wallets. A user does not have to deal with the details of running their own Lightning node or deal with the management of Lightning channels and their Lightning liquidity.
The user can send and receive Lightning bill through his eCash Lightning wallet normally.
Security
The security of a Lightning Mint is less than a self-hosted wallet. The association members responsible for the security of the Bitcoin balance can make off with it. However, compared to a standard Lightning wallet, the security is much higher.
Members may be individuals with a good reputation, with whom users have some trust or personal connection. Similarly, association members can be located in different countries, making the Mint more robust to regulatory intervention.
Cashu and Fedimint
Current implementations of Chaumian eCash mints include:
- https://fedimint.org/ from Fedi
- https://cashu.space/ as an extension of LNbits
Fedimint
Fedimint is an open source protocol developed by the company Fedi. Fedi has well-known supporters and investors. At Fedimint, Bitcoin assets held in escrow are managed by multiple parties. The individual parties are referred to as Guardian and as a group form the Federation.
The custody corresponds to a multisig wallet with multiple participants. In a similar form, the residents of Bitcoin Beach in El Salvador manage the Bitcoin assets of its citizens.
The federated approach of multiple Guardians makes Fedimint particularly well suited for larger communities or platform providers who want to offer the use of the Lightning network for their own customers, users and members.
Cashu
In contrast to Fedimint’s multisig approach with multiple administrators (federation), Cashu follows more of a single-mint setup.
This means that the credit is not managed by multiple members, but only by a single entity, which leads to a reduction in security.
The Cashu Mint system is an extension to an LNbits server. This makes it very easy for any operator of an LNbits server to also run a Mint themselves and enable the use of the Lightning network within their own circle of family and friends.
The Cashu Wallet and Mint System for LNbits, we present in more detail in the article: “Cashu – Lightning eCash Wallet and Mint System“.
The two existing implementations position themselves differently. Fedimint sees itself more as a solution for communities and platform operators and Cashu as a solution for family, friends and acquaintances. Fedimint calls this custody community custody and is thus a solution between self-custody and full custody.
Conclusion: Chaumian eCash for Bitcoin Lightning
Using the Lightning network needs to become easier to convince even more users of its benefits. Custodial wallet solutions today already offer a very simple entry-level solution and work flawlessly. Comparable self-custody wallets are somewhat more sophisticated.
Anyone who has used the Lightning network knows that for all its benefits, running a node and managing a wallet presents some challenges, such as channel unavailability due to forced closures, the unpredictability of on-chain fees, the complexity of channel backup, and the associated need to manage liquidity.
These issues require an experienced node operator to be used effectively and place a significant burden on users of the Lightning network. If this continues to be the case, ordinary mortals may have no choice but to use hosted Lightning wallets, which puts their privacy at risk and exposes them to custody.
With Chaumian eCash for Lightning, users get a good middle ground between self-custodial wallets and full-custodial wallets.